Since the onset of industrialization in 1960, a significant amount of carbon has been released, enough to potentially darken our atmosphere. However, a natural process exists that absorbs this emitted carbon and releases oxygen in return. This process is carried out by the world’s flora, including all plants and trees.
In recognition of this, a system is established known as Carbon Credits to award based on the extent of greenery a country has and the number of trees a farmer owns. These carbon credits can then be purchased by international corporations that are major carbon emitters, or by governments lacking in green spaces. This system aims to incentivize the preservation and expansion of our planet’s greenery.
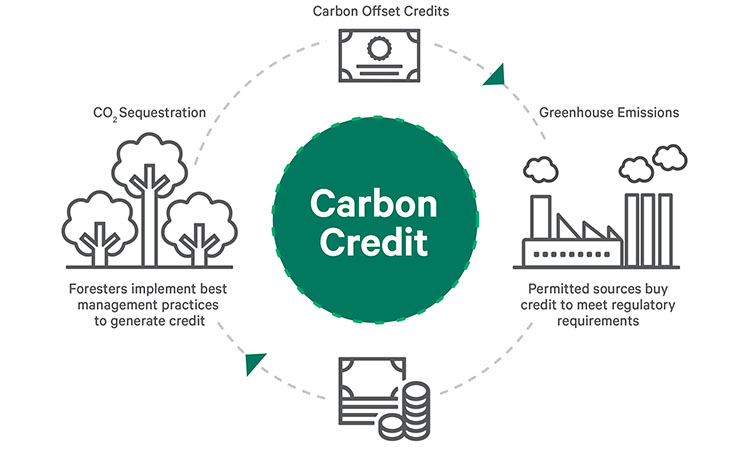
Carbon credits are a way to incentivize the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions and promote carbon sequestration. Carbon credits are a tradable permit that allows the holder to emit one tonne of carbon dioxide or an equivalent amount of greenhouse gases. The holder can sell the permit to another party who can then use it to offset their own emissions1.
India, with the world’s largest area of cropland, is expected to become the leading market for carbon farming credits2. Carbon farming is a promising option that reduces greenhouse gas emissions and stores carbon in soils and degraded rangelands through forests tree plantings and regrowth, carbon storage through incorporation of biochar which is carbon negative, substitution of biofuels for fossil fuels, and other methods2. We at Krushika Framing Community are taking a proactive approach to carbon sequestration through its farming methods. The team is mindful of the amount of carbon that is sequestered through their farming practices. Once local policies are in place, community members will be able to earn proportionate “Carbon credits” for their efforts, which can later be traded at carbon stock exchanges3.
The Indian government has recently notified the Carbon Credit Trading Scheme, 2023 (CCTS 2023) under the Energy Conservation Act, 2001, to develop the country’s first-ever domestic carbon market1. The CCTS 2023 entails the formation of a National Steering Committee or Indian Carbon Market (NSCICM) for the governance and direct oversight of the ICM. The market will be driven by setting Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emission intensity reduction targets in line with India’s Nationally Determined Contributions (NDC) for selected entities to be obligated under CCTS 20231. The CCTS 2023 will provide financial incentives to farmers by allowing those who adopt carbon farming practices to sell their carbon credits2.
Krushika is considering the global and national good in their farming practices. It is essential that we all take responsibility for our actions and work towards a sustainable future3.
3: Mitsui & Co. Global Strategic Studies Institute Monthly Report, February 2023 1: PwC India, Regulatory Insights, July 2023 2: Mitsui & Co. Global Strategic Studies Institute Monthly Report, April 2021
